Induction of general anaesthesia – Core Learning Outcomes
* To conduct safe induction of anaesthesia in ASA grade 1-2 patients confidently
* To recognise and treat immediate complications of induction, including tracheal tube misplacement and adverse drug reactions
* To manage the effects of common complications of the induction process
* To conduct anaesthesia for ASA 1E and 2E patients requiring emergency surgery for common conditions (e.g. uncomplicated appendicectomy or manipulation of forearm fracture/uncomplicated open reduction and internal fixation)
* Demonstrates safe practice behaviours including briefings, checklists and debriefs
* Demonstrates correct pre-anaesthetic check of all equipment required ensuring its safe functioning [including the anaesthetic machine/ventilator in both the anaesthetic room and theatre if necessary]
* Demonstrates safe induction of anaesthesia, using preoperative knowledge of individual patients co-morbidity to influence appropriate induction technique; shows awareness of the potential complications of process and how to identify and manage them
Knowledge
- IG_BK_01 Recalls the pharmacology and pharmacokinetics, including doses, interactions and significant side effects of drugs used during induction of anaesthesia
- * Describes the factors that contribute to drug errors in anaesthesia and strategies used to reduce them
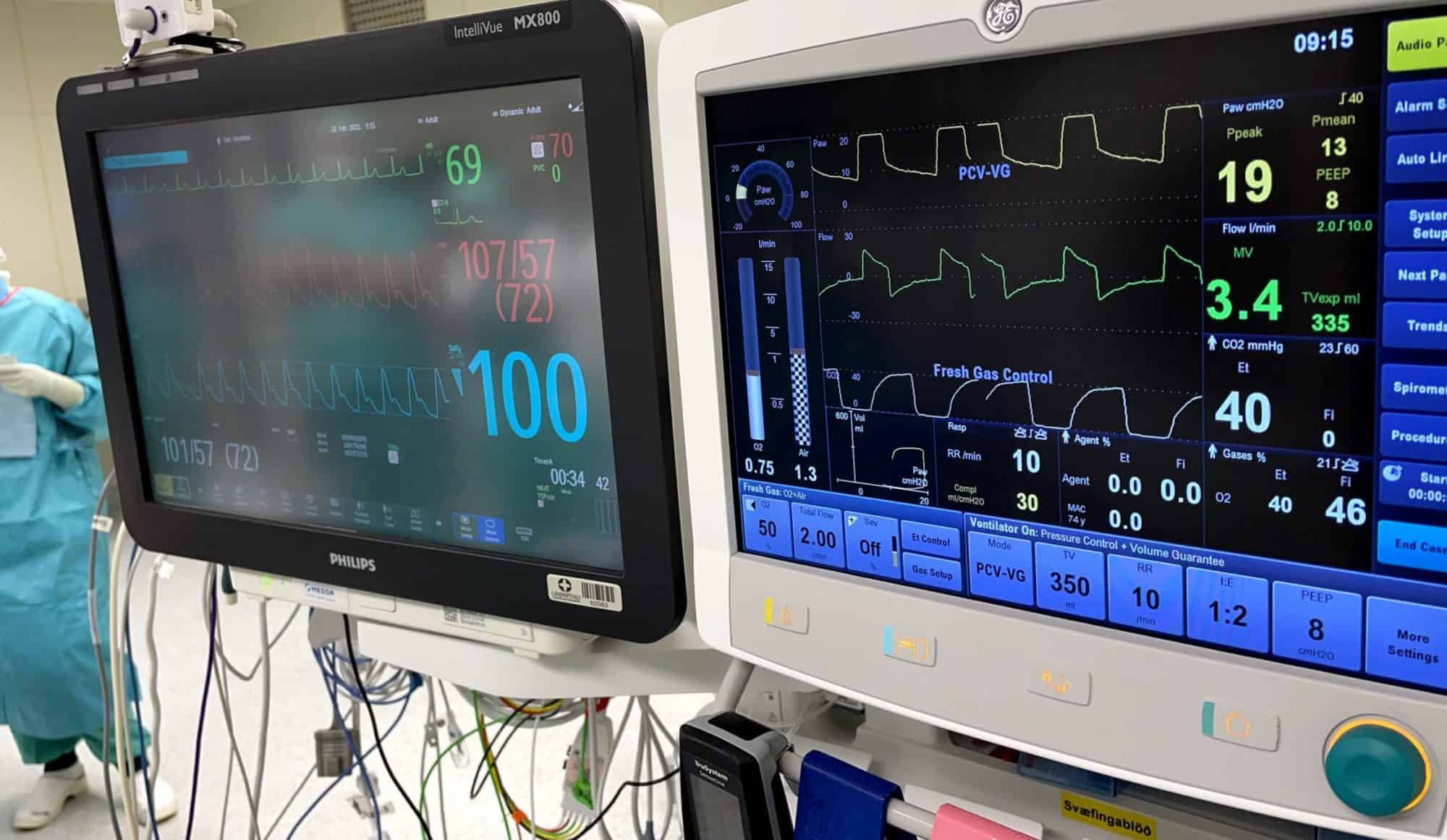
- IG_BK_02 Describes the basic function of monitors
- * Recall consensus minimum monitoring standards and the indications for additional monitoring
- * Explains the functions and safety features of the anaesthetic
- IG_BK_03 In respect of the induction of anaesthesia:
- * Describes the effect of pre-oxygenation and knows the correct technique for its use
- * Explains the techniques of intravenous and inhalational induction and understands the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques
- * Describes the pharmacology of common intravenous induction agents
- * Describes the physiological effects of intravenous induction
- * Describes how to recognise an intra-arterial injection of a harmful substance and its appropriate management
- * Describes anaphylactic reactions and explains the appropriate management including follow up and patient information
- * Lists the factors influencing the choice between agents for inhalational induction of anaesthesia
- * Discusses the additional hazards associated with induction of anaesthesia in unusual places [e.g. Emergency Room] and in special circumstances including but not exclusively: brain injury; full stomach; sepsis; upper airway obstruction
- * Identifies the special problems of induction associated with cardiac disease, respiratory disease, musculoskeletal disease, obesity and those at risk of regurgitation/pulmonary aspiration.
- IG_BK_04 Describes the principles of management of the airway including:
- * Techniques to keep the airway open and the use of facemasks, oral and nasopharyngeal airways and laryngeal maskairways
- IG_BK_05 In respect of tracheal intubation:
- * Lists its indications
- * Lists the available types of tracheal tube and identifies their applications
- * Explains how to choose the correct size and length of tracheal tube
- * Explains the advantages/disadvantages of different types of laryngoscopes and blades including, but not exclusively,the Macintosh and McCoy
- * Outlines how to confirm correct placement of a tracheal tube and knows how to identify the complications of intubation including endobronchial and oesophageal intubation
- * Discusses the methods available to manage difficult intubation and failed intubation
- * Explains how to identify patients who are at increased risk of regurgitation and pulmonary aspiration and knows the measures that minimise the risk
- * Categorises the signs of pulmonary aspiration and the methods for its emergency management
- IG_BK_06 Explains the importance of maintaining the principles of aseptic practice and minimising the risks of hospital acquired infection
Skills
- IG_BS_01 Demonstrates safe practice in checking the patient in the anaesthetic room
- IG_BS_02 Demonstrates appropriate checking of equipment prior to induction, including equipment for emergency use
- IG_BS_03 In respect of the equipment in the operating environment:
- * Demonstrates the functions of the anaesthetic machine including; Performing proper pre-use checks – Changing/checking the breathing system – Replenishing the vaporiser – Changing the vaporiser
- IG_BS_04 Selects, checks, draws up, dilutes, labels and administers drugs safely
- IG_BS_05 Obtains intravascular access using appropriately sized cannulae in appropriate anatomical locations
- * Demonstrates rigorous aseptic technique when inserting cannulae
- IG_BS_06 Demonstrates appropriate placement of monitoring, including ECG electrodes and NIBP cuff
- * Uses monitors appropriately
- * Demonstrates proficiency in the interpretation of monitored parameters
- IG_BS_07 Demonstrates effective pre-oxygenation
- IG_BS_08 In respect of intravenous induction:
- * Explains induction to the patient
- * Prepares drugs for the induction of anaesthesia
- * Administers drugs at induction of anaesthesia
- * Manages the cardiovascular and respiratory changes associated with induction of general anaesthesia
- IG_BS_09 In respect of inhalational induction of anaesthesia:
- * Satisfactorily communicates with the patient during induction
- * Satisfactorily conducts induction
- IG_BS_10 In respect of airway management:
- * Positions the patient for airway management
- * Maintains the airway with oral/nasopharyngeal airways
- * Ventilates the lungs with a bag and mask
- * Inserts and confirms placement of a Laryngeal Mask Airway
- * Successfully places nasal/oral tracheal tubes using direct laryngoscopy
- * Confirms correct tracheal tube placement
- * Uses bougies correctly
- * Secures and protects LMAs/tracheal tubes during movement, positioning and transfer
- * Correctly conducts RSI
- * Correctly demonstrates the technique of cricoid pressure
- IG_BS_11 Demonstrates correct use of oropharyngeal, laryngeal and tracheal suctioningS
- IG_BS_12 Demonstrates failed intubation drill
- IG_BS_13 Manages rapid sequence induction in the high risk situation of emergency surgery for the acutely ill patient
- IG_BS_14 Demonstrates safe perioperative management of ASA 1 and 2 patients requiring emergency surgery